In today’s digital age, printing remains an integral aspect of communication and documentation. From the pages of a book to intricate packaging designs, the world of printing has evolved significantly. With a multitude of printing methods and technologies available, understanding their nuances is essential for anyone interested in producing high-quality printed materials. In this article, we’ll delve into the realm of printing, exploring various methods and technologies that have shaped the way we bring ideas to life on paper.
Introduction to Printing Methods and Technologies
Printing technologies have come a long way since the invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century. Today, printing is a versatile and dynamic field that encompasses a wide array of methods and techniques, each tailored to specific applications and requirements. Whether it’s producing marketing materials, packaging, or artistic creations, mastering the art of printing involves understanding the strengths and limitations of different technologies.
Traditional Printing Methods
Letterpress Printing
Letterpress, one of the earliest printing methods, involves applying ink to raised surfaces and then pressing paper onto them. This technique was once widely used for newspapers, books, and other publications.
Offset Printing
Offset printing employs a series of cylinders and plates to transfer ink from a plate to a rubber blanket and then onto the paper. It’s known for its exceptional color accuracy and is commonly used for mass production.
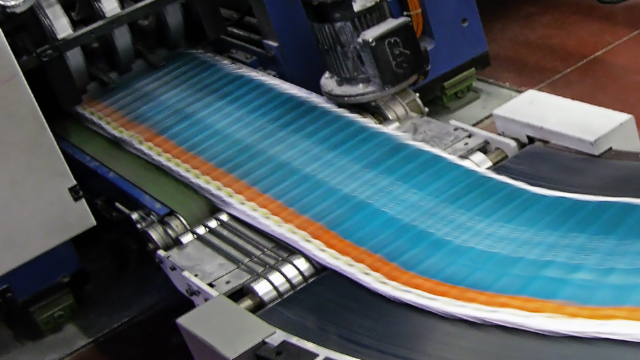
Flexography
Flexography, often used for packaging materials, employs flexible relief plates and fast-drying inks. It’s ideal for printing on uneven surfaces and is a staple in industries such as food packaging.

Gravure Printing
Gravure printing uses etched plates to transfer ink onto paper. It’s popular for high-volume projects and is often seen in magazines, catalogs, and security printing.
Digital Printing Innovations
Inkjet Printing
Inkjet printing propels tiny droplets of ink onto paper. It’s widely used for home and office printing and is favored for its versatility and cost-effectiveness.
Laser Printing
Laser printing uses electrostatic charges and toner to create images on paper. It’s fast, precise, and commonly found in office environments.
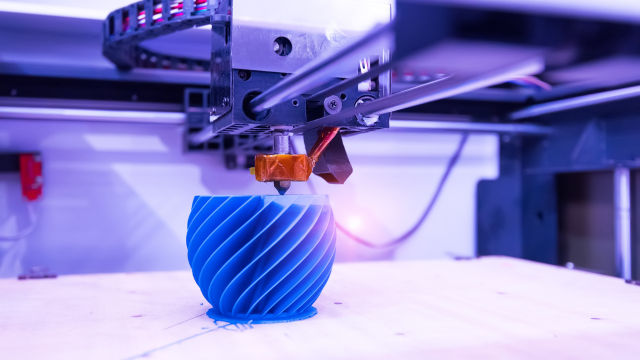
3D Printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, constructs three-dimensional objects layer by layer. It’s revolutionizing industries ranging from healthcare to aerospace.
Nanography
Nanography involves using nanotechnology to enhance traditional offset printing. It offers high quality and speed, making it a promising option for various applications.
Specialty Printing Techniques
Screen Printing
Screen printing involves pushing ink through a mesh screen onto the substrate. It’s used for textiles, signage, and artistic prints.

Dye-Sublimation Printing
Dye-sublimation printing transfers dye onto materials using heat. It’s popular for creating vibrant images on textiles, ceramics, and other substrates.
Embossing and Debossing
Embossing raises designs on paper, while debossing depresses them. These techniques add tactile and visual depth to printed materials.
Foil Stamping
Foil stamping applies metallic or holographic foil to enhance the appearance of printed pieces. It’s often used for branding and luxury packaging.

Evolution of Printing Technologies
The printing industry has experienced remarkable evolution, from mechanical innovations to digital revolutions. Each advancement has brought increased efficiency, quality, and accessibility to the printing process.
Factors Influencing Printing Choices
When choosing a printing method, several factors come into play, including the desired print volume, material type, budget considerations, and the level of color accuracy required.
Sustainability in Printing
In the quest for sustainability, the printing industry is adopting eco-friendly inks, recycling practices, and exploring ways to reduce waste and environmental impact.
Future Trends in Printing
As technology continues to advance, we can expect developments like improved 3D printing capabilities, more efficient digital printing processes, and innovations in sustainable printing materials.
The Artistry of Print
Printing is not only a mechanical process but an art form that allows creativity to flourish. It bridges the gap between digital concepts and tangible, tactile creations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the art of printing involves a deep understanding of the various printing methods and technologies available. Whether you’re creating marketing materials, packaging, or artistic designs, selecting the right printing technique is crucial to achieving the desired results. With a blend of traditional and cutting-edge methods, the world of printing continues to shape how we communicate, inspire, and leave lasting impressions.
FAQs
What is the oldest printing method still in use today?
The letterpress printing method, dating back to Gutenberg’s time, is still utilized by artisans and enthusiasts.
How does 3D printing work in the printing industry?
3D printing builds objects layer by layer from digital designs, enabling rapid prototyping and intricate creations.
Are there eco-friendly printing options available?
Yes, many printing companies now offer eco-friendly inks and materials to reduce the environmental impact.
What printing method is best for detailed and high-color designs?
Digital inkjet printing is known for its precision and ability to reproduce vibrant colors accurately.
How can I incorporate specialty printing techniques into my branding?
Specialty techniques like foil stamping and embossing can add a touch of luxury and uniqueness to your branding materials

